Welcome to the Geoinformation and Big Data Research Laboratory (GIBD) at Penn State, where Big Data and AI meet GIScience.
The Geoinformation and Big Data Research Laboratory (GIBD) in the Department of Geography, College of Earth and Mineral Sciences at The Pennsylvania State University conducts interdisciplinary research on geospatial big data analytics, spatial computing, geospatial artificial intelligence (GeoAI), and cyberGIS within the area of data- and computing-intensive GIScience. The research endeavors are supported by over $1.9 million in direct funding from prestigious sponsors, including the National Science Foundation (NSF), National Institutes of Health (NIH), Taylor Geospatial Institute, NOAA Sea Grant Consortium, NASA, and the South Carolina Department of Social Services, among others. As of 2024, the lab has trained 5 doctoral students, 5 master students, 7 undergraduates, and 1 postdoc, placing four professors.
By developing, synthesizing, and teaching advanced geospatial methods and computing technologies, the mission of GIBD is to 1) advance knowledge discovery and decision making to address a broad range of geographic questions about hazards, public health, population, environment and climate change; 2) train the next generation of GIScientists and geographers with strong problem solving skills through the integration of spatial thinking and computational thinking; and 3) promote spatial data science and geospatial data sharing in geography and a wide range of disciplines such as health science and social science. We strive to achieve the mission through fostering cross-disciplinary collaborative research and education within the lab, across the campus and the nation by engaging researchers from various disciplines who share a common interest in “geospatial”, collaborating with other labs, centers and institutes, and partnering with local community organizations.
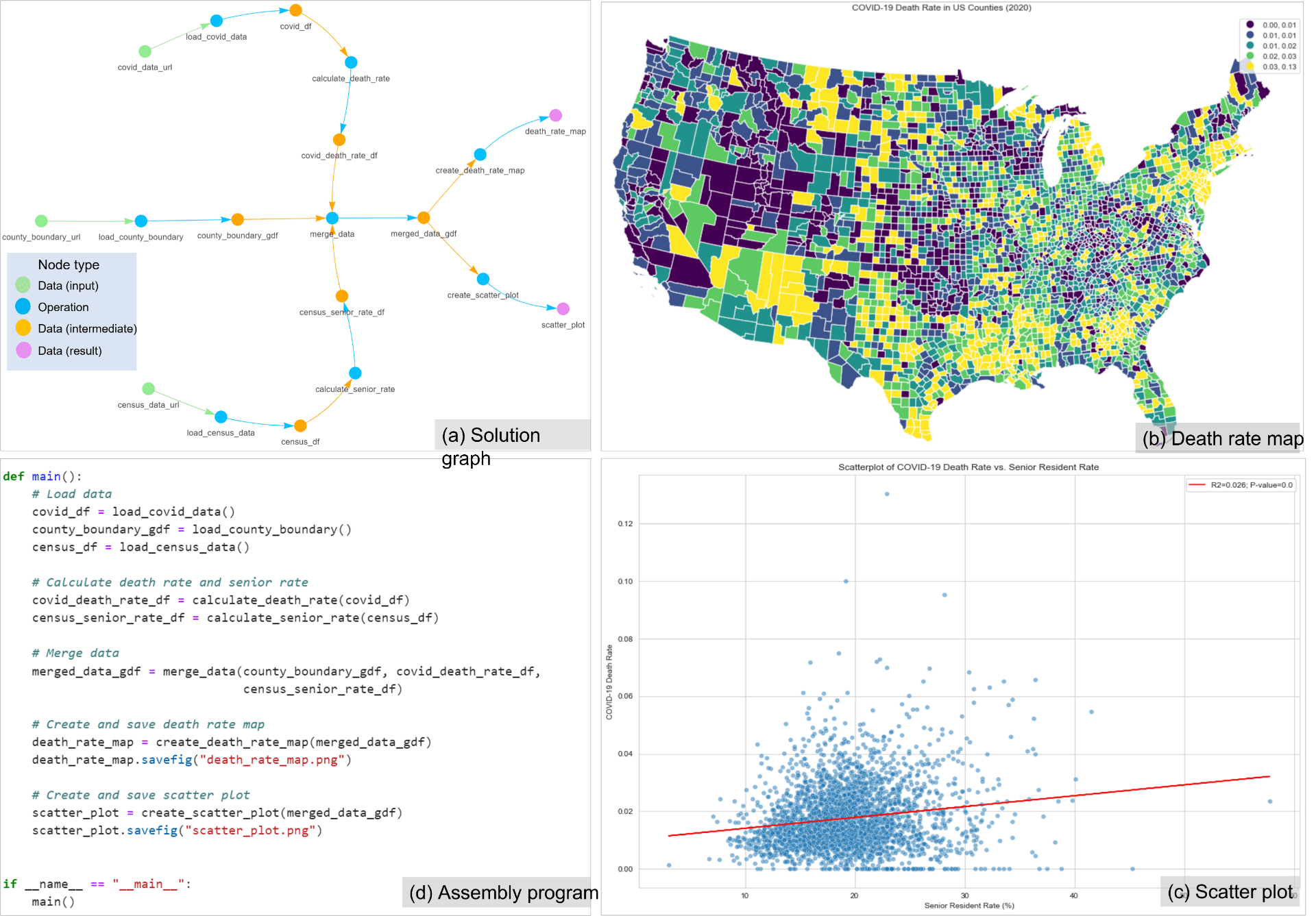
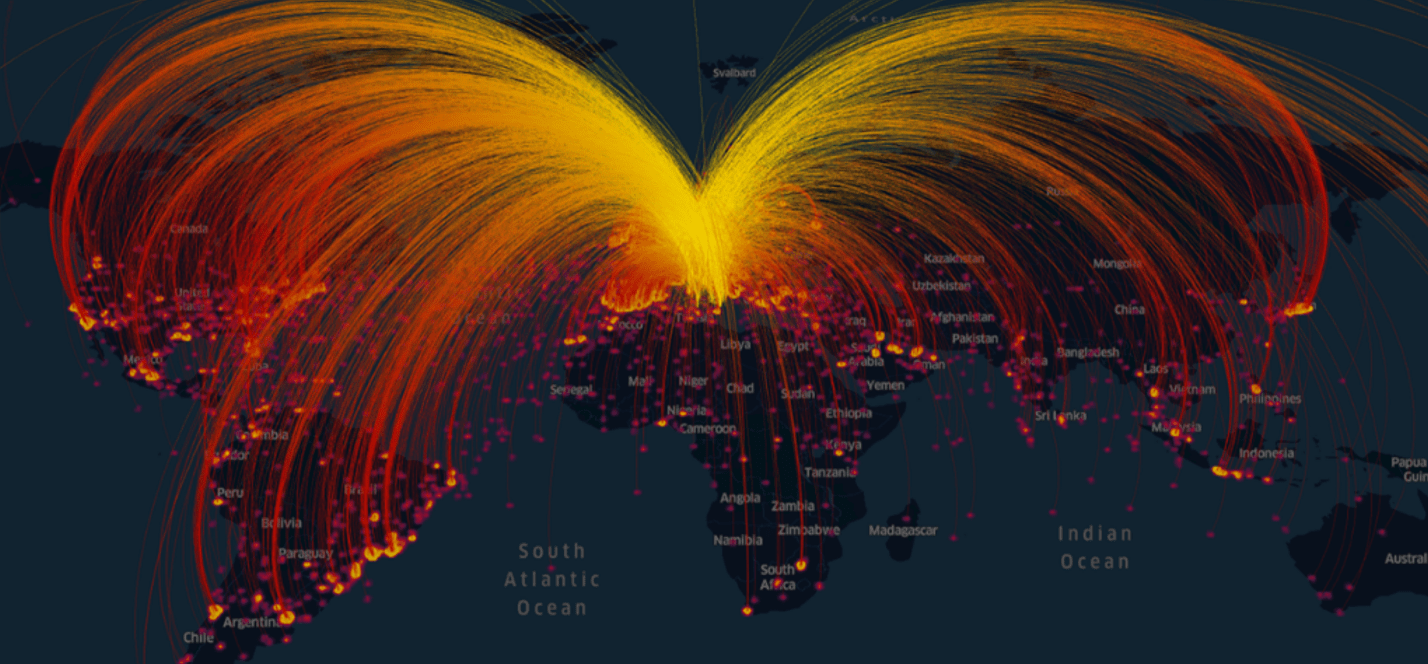
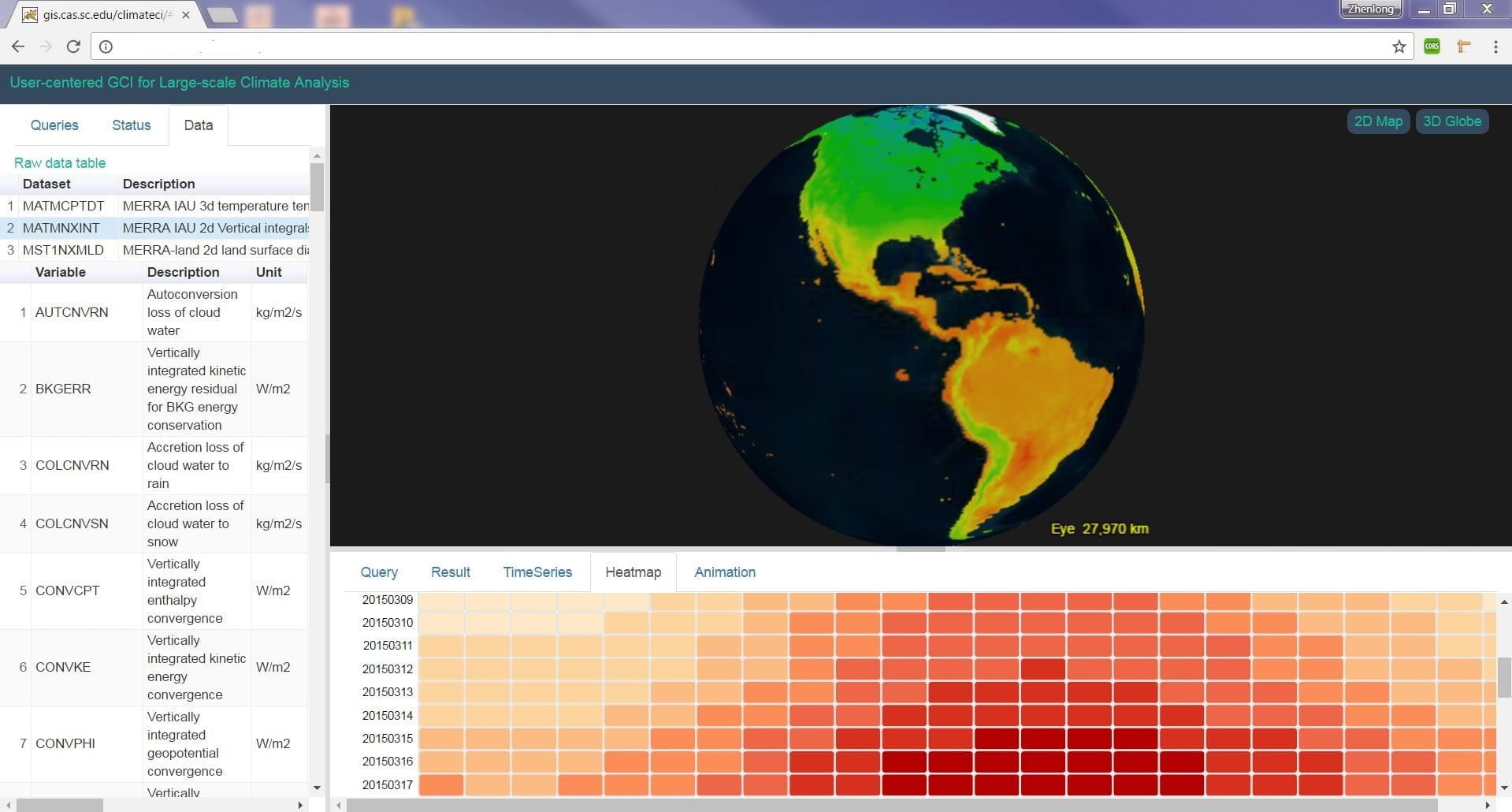
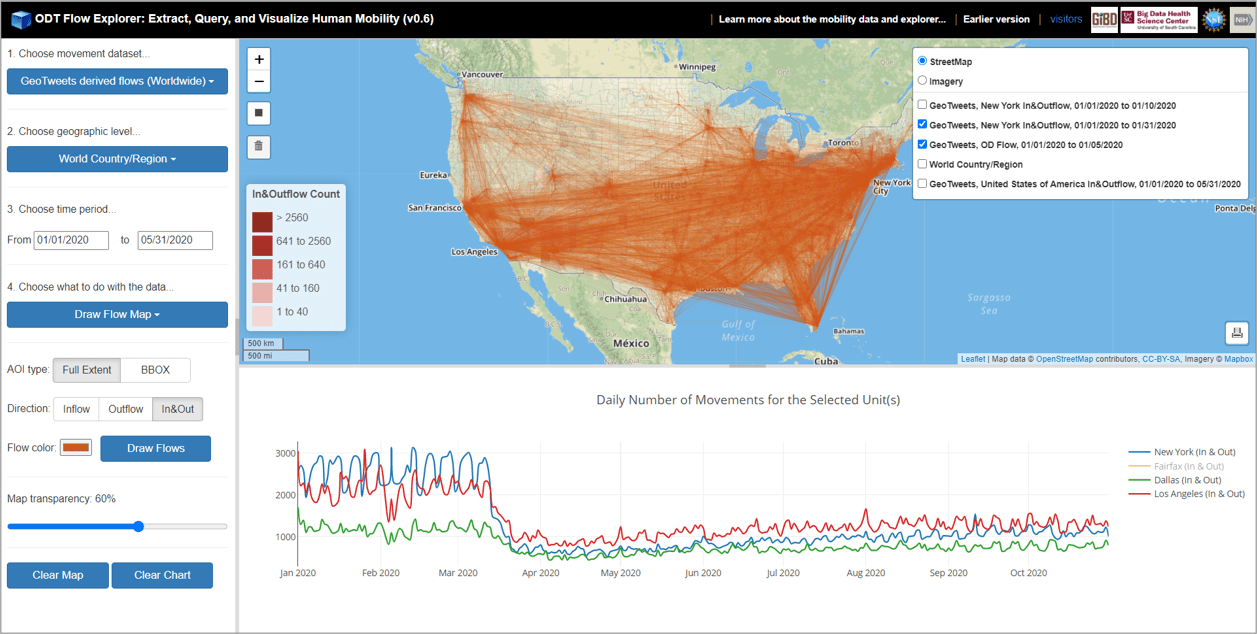
GIBD is equipped with a high-performance big data computing cluster (HPC), serving as a testbed for geospatial big data analytics and computing-intensive research and applications. The lab is also equipped with Deep Learning Workstations powered by high-end NVIDIA Titan XP GPUs for deep learning research and development. On top of the computing infrastructure, GIBD develops a set of innovative parallel processing algorithms, spatiotemporal indices, query analytical tools, and interactive web portals to efficiently manage, analyze and visualize tens of billions of geotagged tweets, terabytes of climate data, and other big data such as mobile location data, taxi trip data, and electronic health records.